Appendicitis ACEP Clinical Policy
Appendicitis: ACEP Clinical Policy
How predictive is WBC in appendicitis?
WBC count > 10K and likelihood of having appendicitis:
- Positive LR 1.59, Negative LR 0.46 (Cardall et al, Acad Emerg Med 2004)
- Positive LR 2.47, Negative LR 0.25 (Andersson, Br J Surg 2004)
Alvarado Score
Alvarado score in predicting appendicitis (Max 10 points)
| Symptom or sign | Point(s) |
|---|---|
| Pain migration | 1 |
| Anorexia-acetone in urine | 1 |
| Nausea/vomiting | 1 |
| RLQ tenderness | 2 |
| Rebound pain | 1 |
| Temperature > 37.3C oral | 1 |
| WBC > 10K | 2 |
| Left shift WBC (>75% PMN) | 1 |
Score:
- 1-4 (appendicitis unlikely)
- 5-6 (possible)
- 7-8 (probable)
- 9-10 (very probable)
However, 0-8% of patients with Score < 5 had appendicitis
Beware of patients <10 yr and >60 yr old for atypical presentations
CT imaging
IV contrast improves ability to detect appendicitis (Jacobs, Radiology 2001)
| CT with... | Sensitivity |
|---|---|
| PO/IV contrast | 91% |
| PO contrast only | 76% |
Addition of oral contrast to CT Abd-pelvis (IV contrast) study is unnecessary (Anderson, Am J Surg 2005)
| CT Technique | Sens | Spec |
|---|---|---|
| Noncontrast | 93% | 98% |
| PO/IV contrast | 93% | 93% |
| Rectal contrast | 97% | 97% |
Imaging in Pediatric Appendicitis
Ultrasound: Appendix >6 mm in diameter, non-compressible appendix, appendiceal tenderness
- Positive LR 17.2-49.5
- Negative LR 0.01-0.14
CT: Unclear about additional benefit of PO/IV contrast. Many give PO/IV because ofless intraperitoneal fat in children (less obvious stranding on noncontrast study)
Kharbanda, Pediatrics 2005: In kids, if 0/5 of the following criteria, then the patient is very unlikely to have appendicitis (negative LR=0.058):
- Nausea
- Right lower quadrant pain
- Difficulty walking
- Rebound tenderness
- Absolute PMN>6,750 (* see Fagan nomogram)
Fagan nomogram
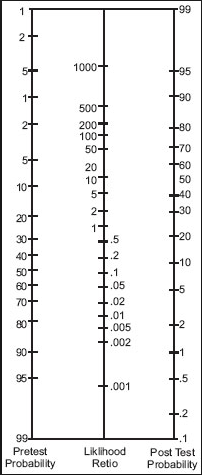
Draw a connecting your pre-test probability and your likelihood ratio. This provides you with your post-test probability.
References
- Howell JM, Eddy OL, Lukens TW, Thiessen ME, Weingart SD, Decker WW; American College of Emergency Physicians.Clinical policy: Critical issues in the evaluation and management of emergency department patients with suspected appendicitis. Ann Emerg Med. 2010 Jan;55(1):71-116. [PubMed]