Dental Infections
Dental Infections
- Dental caries - demineralization of protective enamel and subsequent tooth decay
- Pulpitis - inflammation of pulp secondary to caries
- Periodontitis - loss of supportive bone structure caused by chronic gingivitis
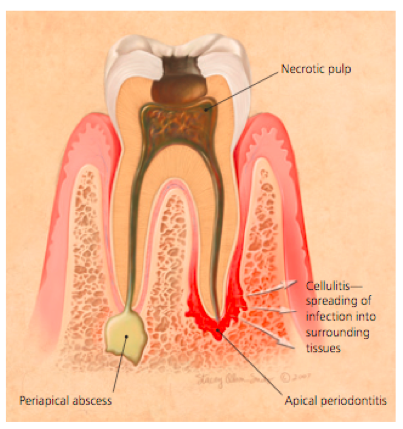
Periapical Abscess
Collection of purulent material at apex of tooth
- Secondary to bacterial invasion from carious destruction of enamel
- History: Progressive pain, thermal sensitivity
- Exam: Caries, decayed tooth, pain with percussion, palpation of apex, gingival swelling, erythema, parulis present, mobile tooth
Treatment:
Antibiotics
- Uncomplicated: Penicillin or Clindamycin
- Complicated: Penicillin + Metronidazole, Piperacillin/Tazobactam, or Clindamycin + Ceftriaxone
Pain control
- I+D if abscess present: probe with 18g needle → purulent → 11 blade stab incision → hemostat blunt dissection +/- packing
- Chlorhexidine 0.1% rinses q2-3h if I & D
Surgical referral, if complicated infection (Ludwig's, Lemierre's Syndrome)
Dentist followup:
Uncomplicated: Generalist in 1-2 days
- Complicated: Oral Surgery as soon as possible
Periodontal Abscess
- Localized purulent infection within the gingival wall of the periodontal pocket
- History: Swelling, pain, loose tooth
- Exam: Purulent discharge, erythema, fluctuant mass, dental extrusion
Treatment:
Pain Control: Dental block, NSAID’s +/- opioids
- I & D abscess as needed: 11 blade stab incision → hemostat blunt dissection +/- packing
Antibiotics:
- Penicillin or Clindamycin
- Chlorhexidine 0.1% rinses q2-3h
Dentist followup
- Generalist in 1-2 days
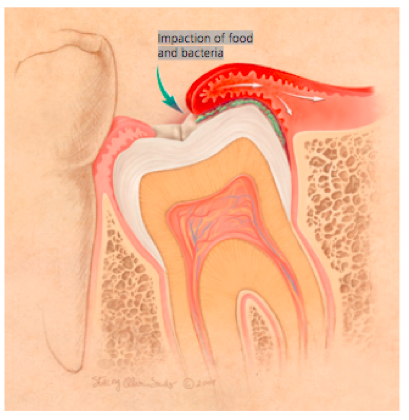
Pericoronitis
- Inflammation +/- infection surrounding impacted or partially erupted tooth
- History: Usually 3rd molar (wisdom tooth), erupting teeth, pain, swelling, halitosis
- Exam: Erythema, swelling, +/- abscess
Treatment: Same as for Periodontal Abscess
- Pain Control: Dental block, NSAID’s +/- opioids
- I & D abscess as needed: 11 blade stab incision → hemostat blunt dissection +/- packing
Antibiotics:
- Penicillin or Clindamycin
- Chlorhexidine 0.1% rinses q2-3h
Dentist followup:
Generalist in 1-2 days
Definitive treatment: Oral Surgery
References
- Nguyen DH, Martin JT. Common dental infections in the primary care setting. Am Fam Physician. 2008 Mar 15;77(6):797-802. [PubMed]