Pertussis
Pertussis
Background
- Bordetella pertussis – Gram negative coccobacillus
- Childhood vaccination confers immunity for 5-10 years
- Incubation period: 7-10 days
CDC Clinical Case Definition of Pertussis
Cough illness lasting ≥ 2 weeks without other apparent cause with 1 or more of:
- Cough paroxysms
- Posttussive emesis
- Inspiratory whoop
| Finding | Positive LR | Negative LR |
|---|---|---|
| Paroxysmal cough | 1.1 (1.1-1.4) | 0.52 (0.14-0.58) |
| Posttussive emesis | 1.8 (1.7-1.9) | 0.58 (0.49-0.80) |
| Inspiratory whoop | 1.9 (1.8-2.4) | 0.78 (0.46-0.87) |
Phases of Pertussis
Phase 1: Catarrhal (week #0-2)
- Nonspecific URI symptoms
- Afebrile or low-grade temperature
- Excessive lacrimation, conjunctival injection
Phase 2: Paroxysmal (week #2-8)
- Paroxysmal coughing spells
- Minimal symptoms between paroxysms
- May hear inspiratory “whoop” especially in children and infants
- Posttussive emesis or syncope
Phase 3: Convalescent (week #8-12)
- Persistent or improving cough
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is not easy
- Dacron swab of posterior nasopharynx (cotton swab is toxic to B pertussis)
- PCR assay (results in 1-2 days, more costly)
- DFA is inexpensive but poorly sensitive and specific (not recommended)
Treatment
- Macrolide (e.g. azithromycin), or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (if allergic)
- Antibiotics decrease duration of pertussis course if given in catarrhal stage (but difficult to differentiate from viral URI)
- Antibiotics in any stage decreases transmission to others.
American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommendation for patients <3 months old:
- If suspect pertussis (basically a cough), swab for pertussis and start azithromycin immediately (10 mg/kg per day in a single dose x 5 days).
Bottom Line
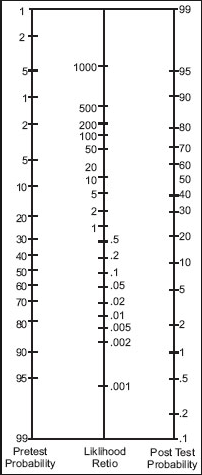
- Positive and negative LR’s for clinical findings are not very helpful.
- More dependent on your pretest probability of patient having pertussis.
- Check if there is a current outbreak in your region.
Fagan Nomogram
References
- Cornia PB, Hersh AL, Lipsky BA, Newman TB, Gonzales R. Does this coughing adolescent or adult patient have pertussis? JAMA. 2010 Aug 25;304(8):890-6. [PubMed]