Elbow Injuries - Radial Head Fracture
Elbow Injuries: Radial Head Fracture
X-ray Views
Elbow XR: AP, lateral, +/- radiocapitellate view
Assess for indirect signs of fracture or dislocation on lateral elbow view.
- Sail sign or posterior fat pad
- Radiocapitellate line misalignment
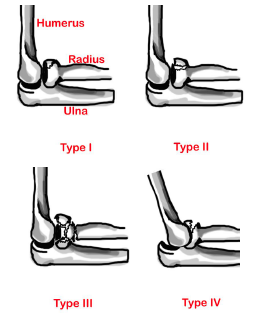
Mason Classification
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| I | Minimally displaced fracture ≤2 mm |
| II | Fracture fragment displaced >2 mm or angulated |
| III | Comminuted and displaced fracture |
| IV | Associated elbow dislocation |
Most common elbow fractures in adults
Operative indications
- >3 mm displacement
- 33% articular surface involvement
- Angulated >30°
- Associated elbow dislocation
Acute Management
- Type I: Sling
- Type II-IV: Long-arm posterior splint with elbow at 90° flexion (after type IV elbow dislocation reduced)
Follow-up Timing
- If operative: ≤3 days
- If non-operative: <1-2 weeks with early mobilization in 48 hours to minimize elbow stiffness
References
- Wheeless’ Textbook of Orthopaedics. Available at: http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/radial_head_frx. Accessed August 1, 2017.
- Orthobullets. Available at: http://www.orthobullets.com/trauma/1019/radial-head-fractures. Accessed August 1, 2017.
- Radiopaedia. Available at: http://radiopaedia.org/articles/radial-head-fractures. Accessed August 1, 2017.
- General Guidelines For Management for Orthopedic Injuries card by the Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Department of Orthopedics