Cholecystitis Diagnostic Test
Cholecystitis - Diagnostic tests
JAMA Clinical Rational Examination Series: Meta-analysis of 17 studies which evaluated role of history, physical, and lab tests in working up cholecystitis
History and Physical Exam
| Finding | (+) LR | (-) LR |
|---|---|---|
| Anorexia | 1.1-1.7 | 0.5-0.9 |
| Emesis | 1.1-2.1 | 0.3-0.9 |
| Fever (>35C) | 1.0-2.3 | 0.8-1.0 |
| Guarding | 1.1-2.8 | 0.5-1.0 |
| Murphy sign | 0.8-8.6 | 0.2-1.0 |
| Nausea | 1.0-1.2 | 0.6-1.0 |
| Rebound | 0.6-1.7 | 0.8-1.4 |
| Rectal tenderness | 0.5-2.3 | 1.0-1.3 |
| Rigidity | 0.3-0.7 | 1.0-1.2 |
| RUQ mass | 0.5-1.2 | 0.9-1.1 |
| RUQ pain | 0.9-2.5 | 0.3-1.6 |
| RUQ tenderness | 1.0-2.5 | 0.2-1.1 |
Laboratory tests
| Finding | (+) LR | (-) LR |
|---|---|---|
| Alkaline phosphatase (AP) >120 U/L | 0.4-1.6 | 0.6-2.0 |
| ALT >40 U/L or AST >48 U/L | 0.5-2.0 | 0.8-1.4 |
| Total bilirubin >2 mg/dL | 0.7-2.3 | 0.7-1.2 |
| All 3 elevated: Total bili, AST, AP | 1.0-2.8 | 0.8-0.9 |
| Any 1 elevated: Total bili, AST, AP | 1.0-1.5 | 0.6-0.9 |
| WBC >10K | 1.2-1.9 | 0.5-1.8 |
| WBC >10K and fever (>35°C) | 0.9-2.8 | 0.8-1.0 |
| WBC ≤10K and no fever (≤35°C) | 0.4-0.7 | 1.4-1.8 |
Use the Fagan nomogram
Note:
- All likelihood ratios (LR) cross or almost cross 1.0.
- This is no history, physical exam, or lab test that would comfortably allow you to rule- out or rule-in cholecystitis.
- Murphy’s sign is perhaps the most useful sign because the +LR has been shown to be as high as 8.6.
Bottom line
Have a low threshold to perform a RUQ abdominal bedside ultrasonography for patients with upper abdominal pain or a fever from an unclear source (especially elder patients). Look for indirect signs of cholecystitis:
- Murphy sign
- Distended gallbladder
- Pericholecystic fluid
- Thickened gallbladder wall
- Gallstones
Fagan nomogram
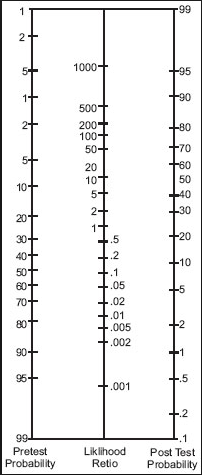
Draw a connecting your pre-test probability and your likelihood ratio. This provides you with your post-test probability.
References
- Trowbridge RL et al. Does this patient have acute cholecystitis? JAMA. 2003, 289(1): 80-6. [PubMed]