Paracentesis for Ascites
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis and Paracentesis
JAMA Rational Clinical Examination Series 2009
Bottom line: It appears safe to perform paracentesis without checking coagulation labs
- 2 prospective studies
- No instances of significant bleeding despite platelet counts <50K and INR >1.5
- 2 cases of minor bleeding
Bottom line: Albumin likely not needed in therapeutic paracentesis
- 9 prospective randomized studies
- Pooled 806 paracentesis procedures: No difference with plasma expansion with respect to encephalopathy and death
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis (SBP) Lab Findings
- Ascites WBC >500 cells/mm3
- Ascites PMN >250 cells/mm3
- Ascites pH <7.35
- Blood-ascites pH gradient >0.1
Ascites fluid analysis to assess for SBP (pooled data)
| Lab Finding | # patients | (+) LR | (-) LR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ascites WBC >1000 cells/mm3 | 508 | 9.1 | 0.25 |
| Ascites WBC >500 cells/mm3 | 717 | 5.9 | 0.21 |
| Ascites PMN >500 cells/mm3 | 1,074 | 10.6 | 0.16 |
| Ascites PMN >250 cells/mm3 | 1,058 | 6.4 | 0.2 |
| Ascites pH <7.35 | 129 | 9.0 | 0.31 |
| Blood-Ascites pH gradient | 129 | 7.1 | 0.30 |
Fagan Nomogram
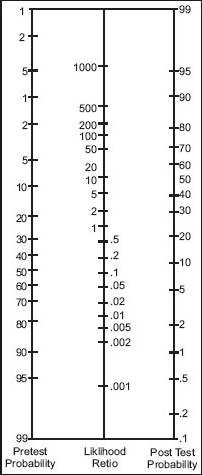
References
- Wilkerson RG, Sinert R.Evidence-based emergency medicine/rational clinical examination abstract: The use of paracentesis in the assessment of the patient with ascites. Ann Emerg Med. 2009 Sep;54(3):465-8. [PubMed]