Pediatric Assessment Triangle
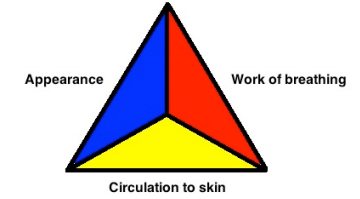
The PAT functions as a rapid, initial assessment to determine “sick” or “not sick,” and should be immediately followed by/not delay the ABCDEs. It can be utilized for serial assessment of patients to track response to therapy.
Appearance: The “Tickles” (TICLS) Mnemonic
| Characteristic |
Normal features |
| Tone |
Move spontaneously, resists examination, sits or stands (age appropriate) |
| Interactiveness |
Appears alert/engaged with clinician or caregiver, interacts well with people/environment, reaches for objects |
| Consolability |
Stops crying with holding/comforting by caregiver, has differential response to caregiver vs. examiner |
| Look/gaze |
Makes eye contact with clinician, tracks visually |
| Speech/cry |
Uses age-appropriate speech |
Work of breathing
| Characteristic |
Abnormal features |
| Abnormal airway sounds |
Snoring, muffled/hoarse speech, stridor, grunting, wheezing |
| Abnormal positioning |
Sniffing position, tripoding, prefers seated posture |
| Retraction |
Supraclavicular, intercostal, or substernal, head bobbing (infants) |
| Flaring |
Flaring of the nares on inspiration |
Circulation of skin
| Characteristic |
Abnormal features |
| Pallor |
White/pale skin or mucous membranes |
| Mottling |
Patchy skin discoloration due to variable vasoconstriction |
| Cyanosis |
Bluish discoloration of skin/mucous membranes |
Relationship of the PAT components to physiological categories and management priorities
| Presentation |
Appearance |
Work of breathing |
Circulation |
Management |
| Stable |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
Specific therapy based on possible etiologies |
| Respiratory distress |
Normal |
ABNORMAL |
Normal |
Position of comfort, O2/suction, specific therapy (e.g. albuterol, diphenhydramine, epinephrine), labs/x-rays |
| Respiratory failure |
ABNORMAL |
ABNORMAL |
Normal or ABNORMAL |
Position head/open airway, BVM, FB removal, advanced airway, labs/x-rays |
| Shock (compensated) |
Normal |
Normal |
ABNORMAL |
O2, peripheral IV, fluid resuscitation, specific therapy based on etiology (antibiotics, surgery, antidysrhythmics), labs/x-rays |
| Shock (decompensated/hypotensive) |
ABNORMAL |
Normal or ABNORMAL |
ABNORMAL |
O2, vascular access, fluid resuscitation, specific therapy based on etiology (antibiotics, vasopressors, blood products, surgery, antidysrhythmics, cardioversion), labs/x-rays |
| CNS/Metabolic dysfunction |
ABNORMAL |
Normal |
Normal |
O2, POC glucose, consider other etiologies, labs/x-rays |
| Cardiopulmonary failure/arrest |
ABNORMAL |
ABNORMAL |
ABNORMAL |
Position head/open airway, BMV with 100% O2, CPR, specific therapy based on etiology (defibrillation, epinephrine, amiodarone), labs/x-rays |
References
- Dieckmann RA, Brownstein D, Gausche-Hill M. The pediatric assessment triangle: a novel approach for the rapid evaluation of children. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2010 Apr;26(4):312-5. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0b013e3181d6db37. [PubMed]
- ER CAST: Courtesy of Dr. Michelle Reina & Dr. Rob Bryant [Source]
